Skin Cancer: What to Know About Melanoma
The most common type of cancer in the U.S. is skin cancer. Approximately 9,500 Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer each day and an estimated one in five Americans will acquire skin cancer during their life.
Fortunately, skin cancer is one of the most preventable and treatable forms of cancer. With increased awareness and education, these numbers can drop dramatically.
Sure, most of us have heard of skin cancer and melanoma. But, what exactly are they?
- Skin cancer is the uncontained growth of abnormal skin cells into malignant tumors as a result of DNA damage, often due to overexposure to sunlight or tanning beds.
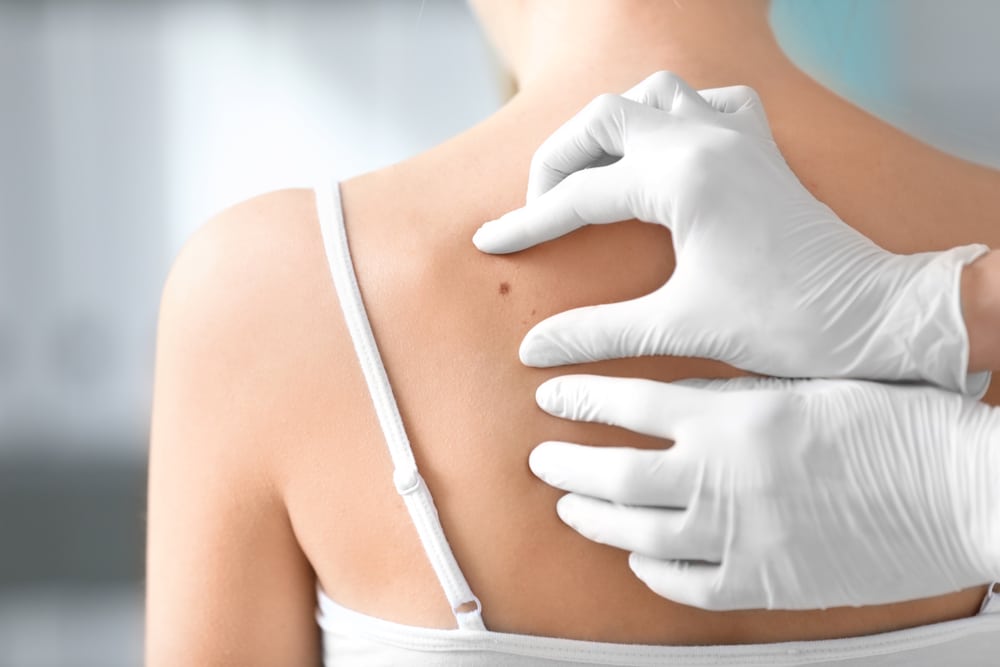
- Melanoma is a particular type of skin cancer that begins in a melanocytes cell. These cells then create darker pigment called melanin. These tumors often appear brown, blue or black, but can be white, pink, or any shade of tan. Out of all types of skin cancers, melanoma causes the most deaths. Approximately one American dies every hour from melanoma.
The importance of shining a light on these diseases is clear — too many people are diagnosed with skin cancer and too many people’s lives are taken because of it. Increased information about prevention, early detection techniques, and life-saving organizations are crucial. Keeping reading for more information about melanoma.
Who is most likely to get melanoma?
- People who have relatives who had melanoma
- People with fair skin who burn and freckles easily
- People with many moles, irregular moles, or large moles
- However, anyone can get melanoma
What causes melanoma?
- UVA and UVB ray exposure: A lot of exposure to the sun, sun lamps, or tanning beds increases one’s chances of developing melanoma or other types of skin cancer. Exposure to UV rays causes nearly 90 percent of melanoma cases.
- Moles: Melanoma may start very suddenly, so it’s essential to know the normal color and sizes of the moles on your body.
- Genetics: A mutated gene can be passed on through generations. Know your family history in regards to skin cancer (as well as all cancers, chronic illnesses, and diseases).
What are the warning signs of melanoma?
- Atypical moles (moles that look different from other moles)
- Asymmetrical moles (healthy moles should be symmetrical)
- Mole(s) that change in any way
- Uneven or scalloped borders around the mole
- Multicolored moles
- Moles that are larger in diameter than an eraser on a pencil
How can you prevent melanoma?
- Wear sunscreen every day
- Avoid sunburns
- Wear SPF 30 or higher sunscreen
- Stay in the shade as much as possible when outside
- Don’t use UV tanning beds or sun lamps
- Examine your skin monthly
- Visit your doctor annually for a skin exam
How do you check yourself or a loved one for melanoma?
Early detection improves your chances of treating Melanoma. The prognosis is worse once melanoma cells reach vital organs. So, make sure you examine your body regularly for atypical moles. Here are step-by-step instructions about how to conduct a head-to-toe examination, provided by the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Prevent skin cancer by using sunscreen and limiting your time in the sun. If you or a loved one has been recently diagnosed with melanoma, here are some important questions to ask your doctor.

Join our Senior Wellness Society for the latest news on Medicare and tips for healthy living in San Diego!
Sign up now ›Are you looking for specialized medical care in San Diego?
Our directory has more than 850 doctors in San Diego County of various specialties who are available to help you.
Find a doctor